A) The plasma membrane becomes highly permeable to sodium ions and depolarization results.
B) As sodium ions enter, the inside of the plasma membrane becomes more negative.
C) At the peak of depolarization, sodium channels begin to close and potassium channels open.
D) In repolarization, potassium ions flow out of the cell.
E) Action potentials occur according to the all-or-none principle.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enteric nervous system consists of plexuses within the walls of the
A) brain.
B) spinal cord.
C) digestive tract.
D) urinary bladder.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The motor (efferent) division of the peripheral nervous system
A) is a division of the CNS.
B) regulates the digestion of food.
C) transmits impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscle.
D) has nerve cell bodies located in ganglia near the spinal cord and brain.
E) detects a stimulus.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cell bodies of the peripheral nervous system are located in
A) ganglia.
B) Schwann cells.
C) the motor division.
D) the sensory division.
E) nerves.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Most unipolar neurons are ____________ neurons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the correct definition. -Action Potential
A) a small change in the resting membrane potential confined to a small area
B) a charge difference across the plasma membrane when the cell is in an unstimulated state
C) a larger change in resting membrane potential that spreads over entire surface of a cell
D) membrane becomes more positive when sodium ions diffuse into cell
E) return to the resting membrane potential
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following concerning concentration differences across the plasma membrane. -requires ATP
A) concentration of potassium
B) concentration of sodium and chloride
C) negatively charged proteins
D) sodium/potassium pump
E) plasma membrane is more permeable to this ion because of leak ion channels
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nervous system
A) monitors internal and external stimuli.
B) transmits information in the form of action potentials.
C) interprets or assesses information.
D) maintains homeostasis.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately describe events that occur as a result of a local potential reaching threshold?
A) Activation gates of Na+ ion channels begin to close.
B) Inactivation gates of Na+ ion channels begin to open.
C) A positive feedback cycle develops in which depolarization causes activation gates of Na+ ion channels to open.
D) K+ ion channels begin to close.
E) Inactivation gates of Na+ ion channels begin to open and a positive feedback cycle develops in which depolarization causes activation gates of Na+ ion channels to open.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Local hyperpolarization in a synapse is called a(an)
A) excitatory postsynaptic potential.
B) resting membrane potential.
C) inhibitory postsynaptic potential.
D) gap junction potential.
E) action potential.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptor molecules
A) are nonspecific.
B) are always lipids.
C) attach to the synaptic cleft.
D) determine whether a neurotransmitter will be excitatory or inhibitory.
E) are not attached to ligand-gated channels.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why isn't an action potential transmitted from a postsynaptic membrane to a presynaptic terminal?
A) Presynaptic terminals have no acetylcholine receptors.
B) Presynaptic neurons do not have a resting membrane potential.
C) Acetylcholine can only diffuse in one direction across the synaptic cleft.
D) Synaptic vesicles in the postsynaptic membrane are inactive.
E) Acetylcholine is destroyed too fast.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Depolarization of the nerve cell membrane occurs when there is a rapid influx (inflow) of
A) potassium ions.
B) chloride ions.
C) calcium ions.
D) sodium ions.
E) proteins.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Gray matter has little myelination, whereas white matter has abundant myelination.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by ____________ cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two action potentials arrive simultaneously at two different presynaptic terminals that synapse with the same postsynaptic neuron,
A) the direction of the action potential is reversed.
B) temporal summation occurs.
C) spatial summation occurs.
D) hyperpolarization occurs.
E) threshold is never reached.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Enkephalins produce presynaptic inhibition in neurons transmitting pain signals. Increased levels of enkephalins will
A) increase awareness of pain.
B) decrease awareness of pain.
C) increase amount of pain.
D) decrease amount of pain.
E) have no effect on awareness or amount of pain.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
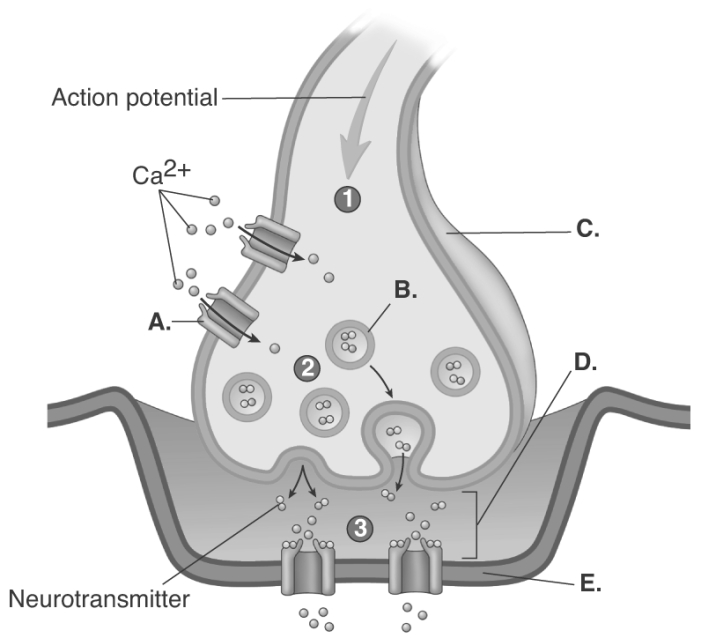 -The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse. What does "E" represent?
-The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse. What does "E" represent?
A) postsynaptic membrane
B) synaptic cleft
C) synaptic vesicle
D) voltage-gated calcium channel
E) presynaptic terminal
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the correct definition. -depolarization
A) a small change in the resting membrane potential confined to a small area
B) a charge difference across the plasma membrane when the cell is in an unstimulated state
C) a larger change in resting membrane potential that spreads over entire surface of a cell
D) membrane becomes more positive when sodium ions diffuse into cell
E) return to the resting membrane potential
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Action potentials are conducted more rapidly when transmission is
A) from node to node on a myelinated axon.
B) on a small diameter axon.
C) on an unmyelinated axon.
D) from internode to internode.
E) from internode to node on a myelinated axon.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 155
Related Exams