A) $18 per hour.
B) $36 per hour.
C) $3 per hour.
D) $108 per hour.
E) $648 per hour.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An improvement in technology that increases the marginal product will shift the demand for labor curve to the left.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best explains the decline in marginal revenue product (MRP) ?
A) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: Labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital) , total product become smaller and smaller.
B) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital) , marginal product become smaller and smaller as defined by the law of diminishing returns.
C) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital) , marginal utility becomes smaller and smaller.
D) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital) , marginal revenue product (MRP) become larger and larger.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a competitive labor market, marginal revenue product equals marginal product times the wage rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes marginal revenue product (MRP) ?
A) MRP is the level of total revenue generated by total employment of labor and capital.
B) MRP is the change in total revenue caused by a one-unit increase in output.
C) MRP is the change in total revenue caused by a one-unit increase in a variable input such as labor.
D) MRP is total revenue divided by the total quantity of a variable input used.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there are 100 identical firms producing package delivery services. One of the firms finds that when it has to pay a wage rate of $7, it hires 20 delivery people. The firm charges an average price of $10 to deliver a package. From this information, we know that the package delivery industry is hiring a total of:
A) 100 workers.
B) 200 workers.
C) 700 workers.
D) 2,000 workers.
E) 10,000 workers.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Dividing the economic pie more equally may reduce the size of the economic pie." This argument is characterized as:
A) untrue.
B) a form of discrimination.
C) a conflict between equity and efficiency.
D) a conflict between full employment and economic growth.
E) b and c.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following program(s) examples is (are) in-kind assistance to fight poverty in the United States?
A) b and e.
B) Medicaid.
C) Unemployment benefits.
D) Temporary Assistance to Needy Families (TANF) .
E) SNAP (food stamps) .
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A technological advance that increases the productivity of teachers can be expected to have what effects on the equilibrium labor market for teachers?
A) Wages will rise, and quantity of labor will fall.
B) Wages will rise, and quantity of labor will rise.
C) Wages will fall, and quantity of labor will fall.
D) Wages will fall, and quantity of labor will rise.
E) Wages and quantity of labor will remain the same.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the demand for a product will shift the demand curve for labor producing the product to the right.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a competitive labor market, the change in total labor costs divided by the change in labor is always equal to:
A) one.
B) the wage rate.
C) the number of firms in the market.
D) the change in total revenue.
E) the competitive market price of the output.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10-3 Supply and demand curves for food servers 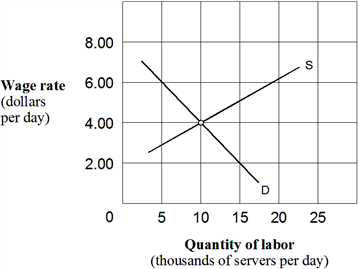 If the equilibrium wage rate in Exhibit 10-3 increased, the cause could be that:
If the equilibrium wage rate in Exhibit 10-3 increased, the cause could be that:
A) the supply of labor increased.
B) the demand for labor decreased.
C) either the demand for labor increased or the supply of labor decreased.
D) none of the above.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be a human capital investment?
A) On-the-job training programs.
B) Health care programs.
C) Formal education.
D) All of the above.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10-5 A perfectly competitive labor market 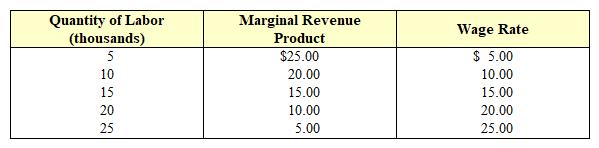 In Exhibit 10-5, how many thousands of workers are firms willing to hire?
In Exhibit 10-5, how many thousands of workers are firms willing to hire?
A) 20.
B) 10.
C) 15.
D) All 30 workers.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A technological advance that increases labor productivity will:
A) lower wages.
B) decrease the demand for labor as fewer workers are needed.
C) decrease the supply of labor as fewer workers are needed.
D) increase the demand for labor as MP rises.
E) decrease the demand for labor as MP falls.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dividing the change in total revenue by the change in labor gives:
A) marginal product of labor.
B) marginal revenue product of labor.
C) the price of the output.
D) demand for the output.
E) economic efficiency.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10-1 Labor and output data 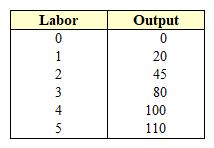 In Exhibit 10-1, the marginal product of the 3rd unit of labor is equal to:
In Exhibit 10-1, the marginal product of the 3rd unit of labor is equal to:
A) 80.
B) 45.
C) 35.
D) 100.
E) 25.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since the demand for labor depends on the demand for the product labor produces, the demand for labor is called:
A) primary demand.
B) secondary demand.
C) dependent demand.
D) derived demand.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal cost of labor for a perfectly competitive firm is given by:
A) the change in total revenue that results from employing an additional worker.
B) the market wage rate.
C) its marginal revenue product curve.
D) the demand curve for labor.
E) the marginal product of labor.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10-3 Supply and demand curves for food servers 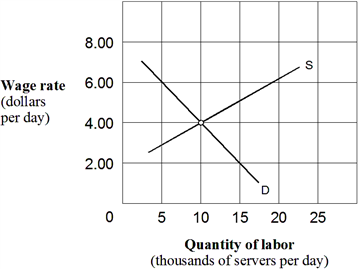 In Exhibit 10-3, suppose that in the interest of boosting incomes of the working poor, Congress imposes a minimum wage of $6.00 per hour. This minimum wage rate creates a(n) :
In Exhibit 10-3, suppose that in the interest of boosting incomes of the working poor, Congress imposes a minimum wage of $6.00 per hour. This minimum wage rate creates a(n) :
A) new labor market equilibrium.
B) excess demand for labor of 10 thousand food servers.
C) excess supply of labor of food servers.
D) situation of full employment for food servers.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 185
Related Exams