A) Phenotype
B) Genotype
C) Dominance
D) Genes
E) None of the answers are correct
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Chi-square test is used to prove that a hypothesis is correct.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which definition below is the best definition for probability?
A) The number of times a coin is flipped
B) The number of times homozygotic recessives appear through successive generations of a family as compared to heterozygotes
C) The chance that an outcome will occur in the future
D) The frequency at which homozygous recessive traits are seen in an individual mating
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question refers to the Punnett square below. Which letter represents a homozygotic dominant progeny? 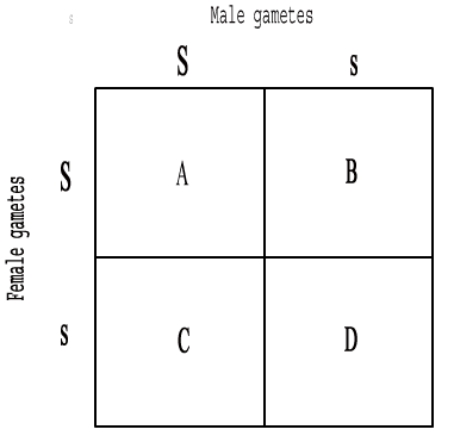
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct regarding the blending hypothesis of inheritance?
A) It suggested that hereditary traits blended from one generation to the next
B) It was possible for the blending to change the trait from one generation to the next
C) It was supported by early research by Joseph Kölreuter
D) It was the prevailing hypothesis of inheritance prior to Mendel
E) All of the answers are correct
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mendel's work with single-factor crosses resulted in the development of which of the following?
A) Law of segregation
B) Law of independent assortment
C) Theory of natural selection
D) Law of biological evolution
E) All of the answers are correct
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A coin is flipped 100 times, with a result of 53 heads and 47 tails. The deviation between the observed numbers and the expected 50-50 results is called _________.
A) Probability
B) Degrees of freedom
C) Goodness of fit
D) Random sampling error
E) Standard error
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two dihybrid pea plants (both tall and with purple flowers) are mated. The cross resulted in 9866 progeny, of which 5550 were tall with purple flowers. What are the expected ratios of the other phenotypic classes?
A) 1850 Short/white flower 616 Tall/white flower 1850 Short/purple flower
B) 1850 Short/white flower 1850 Tall/white flower 1850 Short/purple flower
C) 616 Short/white flower 1850 Tall/white flower 1850 Short/purple flower
D) 5550 Short/white flower 5550 Tall/white flower 5550 Short/purple flower
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The probability that one event or another will occur is based on which of the following?
A) Sum rule
B) Product rule
C) Chi-square test
D) Binomial expansion
E) Random sampling error
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be used for many different purposes, including determining paternity. PCR amplifies specific DNA sequences from complex mixtures and can be used to amplify sequences that although they may not have any known function may have several unique sizes and these different forms are inherited according to the Law of Segregation. Below is a diagram of an agarose gel of PCR samples from a mother, and several children. Which letters represent children that could be biologically related to the mother? 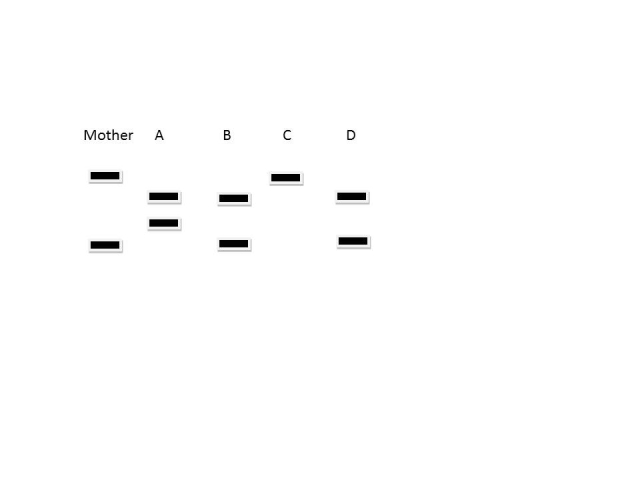
A) A, B, and C
B) All of the children could be related to the mother
C) B, C, and D
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An individual who has two different alleles for a trait is called ____________.
A) Haploid
B) Homozygous
C) Heterozygous
D) Isozygous
E) True-breeding
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An allele that produces an inactive enzyme would be classified as what kind of allele?
A) Loss of function
B) Gain of function
C) Dominant
D) These do not occur and therefore there is no classification for them.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Huntington's Disease is a fatal syndrome caused by a mutation in the HD gene. The disease has an average age of onset of 35 and the majority of individuals that are affected are heterozygotes. What is the probability that a 25 year old woman with no symptoms and who is the daughter of a man that has HD and a mother who does not will have a child that will have the mutant HD allele?
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The results that demonstrated that traits were not blended were the ones where
A) The F2 plants were selfed
B) The true-breeding parents were crossed
C) The F1 generation plants were selfed
D) None of these experiments refuted the blending hypothesis
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The chance that a future event will occur is called ____________.
A) Probability
B) Goodness of fit
C) Degrees of freedom
D) Random selection
E) All of the answers are correct
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _______ is the observable characteristics of an individual.
A) character
B) genotype
C) phenotype
D) dominant trait
E) recessive trait
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a dihybrid cross using Mendelian inheritance, if both parents are heterozygous for both traits, what will be the phenotypic ratio of their offspring?
A) 3:1
B) 1:2:1
C) 1:1
D) 9:3:3:1
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a Punnett square is used to visualize a three-factor cross (trihybrid cross) how many boxes would be inside of the square?
A) 3
B) 8
C) 48
D) 64
E) Can't be determined
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the progeny of a mating of pea plants have the following ratios 1342 smooth seed/green pod, 447 wrinkled seed/yellow pod, 429 smooth seed/ yellow pod, 1361 wrinkled seed/green pod what are the genotypes of the parents?
A) Parent 1: Homozygous for seed shape and pod color Parent 2: Heterozygous for seed shape and homozygous for pod color
B) Both parents are heterozygous for seed shape and pod color
C) Parent 1: Heterozygous for seed shape and pod color Parent 2: Homozygous seed shape and heterozygous for pod color
D) Parent 1: Heterozygous for both seed shape and pod color Parent 2: Homozygous for both seed shape and pod color
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be used to determine the probability of three independent events in order?
A) Sum rule
B) Product rule
C) Chi-square test
D) Binomial expansion
E) Random sampling error
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 65
Related Exams